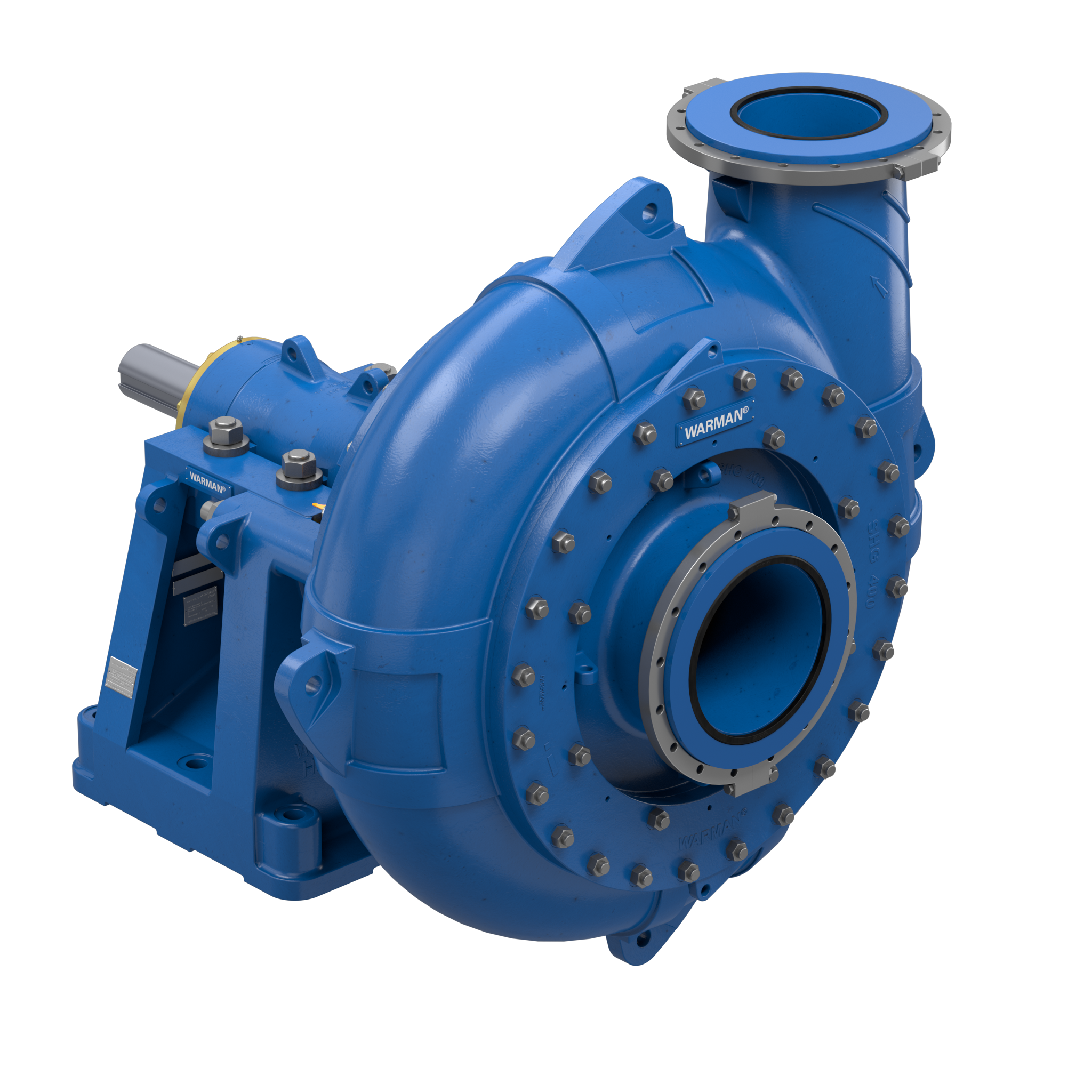
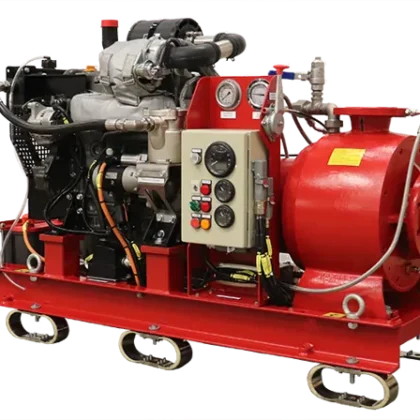
A marine dredge pump is a specialized, heavy-duty centrifugal pump designed to transport a mixture of water and solid materials, known as a slurry. It is the heart of any dredging operation, built to withstand the extreme abrasive forces of pumping sand, silt, gravel, clay, and rock. Unlike standard centrifugal pumps, every component of a dredge pump is engineered for exceptional durability and wear resistance.1
Working Principle
The dredge pump operates on the same centrifugal principle as other pumps, using a rotating impeller to create velocity and pressure.2 However, its design is optimized for handling a two-phase mixture (solids and water).
- Suction: The pump is installed at the end of a suction pipe or within the hull of the dredger.3 It draws the slurry from the seabed.
- Impeller: The robust impeller, with its thick, wide vanes, imparts energy to the slurry, accelerating it towards the discharge. The impeller’s design allows large solids to pass through without clogging.4
- Discharge: The high-velocity slurry is then directed into a volute or casing, where the velocity is converted into pressure, pushing the mixture through a discharge line to the desired location (e.g., a hopper, a disposal site, or a land reclamation area).
Key Components and Wear-Resistant Materials
The longevity of a dredge pump is entirely dependent on the materials and design of its internal “wet end” components.
- Casing: The main body of the pump.5 It is lined with replaceable wear plates or liners to protect the main casing from abrasion. These liners are a crucial spare part.
- Impeller: The single most important component, often made of high-chromium cast iron or other proprietary hard alloys. The vanes are thick and designed with a wide-open passage to handle large solids.
- Shaft and Bearings: The shaft is massive to handle the torque, and the bearings are robustly sealed and often oil-lubricated to protect them from the harsh environment.
- Sealing System: The seal where the shaft exits the casing is critical. It can be a gland packing system (using grease and flushing water) or a more advanced mechanical seal to prevent the abrasive slurry from leaking and damaging the bearings.
Marine Applications
Dredge pumps are the engine of various dredging and mining operations.6
- Trailing Suction Hopper Dredgers (TSHD): These vessels have a pump that sucks up material from the seabed while moving, depositing it into a hopper.7
- Cutter Suction Dredgers (CSD): A powerful cutter head at the end of a ladder loosens the material, and a pump then sucks up the resulting slurry.
- Land Reclamation: Pumping material from a borrow pit to build new land.8
- Harbor and Channel Maintenance: Removing silt and sediment to maintain shipping channels.9
- Seabed Mining: Pumping minerals from the ocean floor.
Maintenance and Spares
Due to the continuous abrasion, a dredge pump’s maintenance is a key part of its operational cycle.10
- Wear Monitoring: Regular inspection and measurement of the impeller and liner thickness are vital. The pump is often designed with easy access for this purpose.
- Liner and Impeller Replacement: The “wet end” parts are designed to be replaceable.11 A pump’s lifespan is defined by how often these parts can be changed.
- Sealing: Gland packing must be properly adjusted and flushed with clean water to prevent slurry from reaching the bearings.
Common Spares include:
- Impellers: A spare impeller is the most critical and expensive spare part.
- Wear Plates / Liners: The replaceable inner linings of the casing.
- Shaft Seal Kits: Spare gland packing or mechanical seal components.
- Bearings: Spares for the heavy-duty shaft bearings.
- Pump Shaft: A spare shaft may be carried for deep overhauls.
A marine dredge pump is more than just a pump; it is a highly specialized piece of engineering whose robust design directly translates into project efficiency and profitability in a demanding industry.
We offer an extensive range of marine engine brands and their associated spare parts, providing comprehensive solutions for both main propulsion and auxiliary power needs across diverse vessel types. Our supply capability covers various generations and models, ensuring support for a wide array of marine applications.
Featured Brands and Engine Series/Models:
SULZER:
- Two-Stroke Engines:
- RD/RND Series: RD68, RND76, RND76M, RND90, RND90M (Classic large-bore, low-speed engines, still in operation).
- RLA/RLB Series: RLA(B)56, RLA(B)66, RLA(B)76, RLB90 (Developed two-stroke designs).
- RTA/RT-Flex Series: RTA38, RTA48(T), RTA52, RTA58, RTA62, RTA72, RTA76, RTA84, RTA84M, RTA84C, RTA96 (Modern, fuel-efficient, electronically controlled two-stroke engines).
- Four-Stroke Engines:
- Z Series: ZL40/48, 16ZAV40S (Medium-speed engines).
- RF Series: RF44, RF56 (Often used for auxiliary power or generator sets).
- TAD Series: TAD36, TAD48 (For specific applications).
MAN (including pre and post-MAN B&W models):
- Two-Stroke Engines (KZ, KSZ, K, L, S, MC/MC-C, ME/ME-C): 40/54A, 52/90N, 57/80C, KZ57/80F, KSZ70/125, KSZ78/155, 90/160A, 52/55L, 58/64, 90/190C, L60/105E, 70/120E, 70/125C, L, KSZ78/155A, KSZ70/125B, L52/55A, 40/45 (A broad spectrum covering main propulsion and auxiliary engines).
B&W (Burmeister & Wain – prior to MAN B&W merger):
- MC/MCE Series: L35MC, L60MC, L80MC, L55GFCA, L80GFCA, L80GB, 74VT2BF, K62EF, K74EF, K84EF, K45GFC, K67GFK, K80GFK, K90GFS, 45HU, L70MC (Various generations of two-stroke diesel engines).
- MC-C/ME-C Series: L50MC, S60MC, S70MC, K80MC, S80MC, K90MC-C, L67GFCA, L90GB (Electronically controlled and conventional two-stroke engines).
- VT2BF/EF Series: 50VT2BF, 62VT2BF, K84EF (Older models still in service).
MITSUBISHI:
- UEC/UET Series: UEC37L/LA/LS, UEC45HA, UEC60L/LA/LS, UEC45L/LA/LS, UET45/75C, UEC52/125H, UEC52L/LA/LS, UET45/80D, UEC52/90D, UEC(T)52/105D, UEC45/115H, UEC37/88H, UEC37H (Mitsubishi’s proprietary two-stroke and some four-stroke engine series).
PIELSTICK:
- PA Series: PA6, PC3, PC2-2, IHI PC2-5, PC4, PC2-6, PC4-2L, PC4-570, PA5 (High-speed, compact four-stroke engines, commonly used for generator sets or auxiliary propulsion).
AKASAKA:
- UET/UEC/DM/AH Series: UET45/80D, UEC52/105D, DM51SS, UEC 60/150H, UEC 60H, A31, A34, A37, A41, AH27, AH28, AH30, AH36, AH38, AH40, DM30, DM36, DM38, DM46, DM47 (A prevalent engine brand, particularly in Japanese-built vessels).
DEUTZ:
- RBV/TBD/BVM Series: RBV8M358, RBV8M540, RBV16M640, TBD620L6, BVM350, BVM540, BF6M716 (Various four-stroke medium- and high-speed diesel engines for auxiliary and smaller main propulsion applications).
HANSHIN:
- EL/LH/LU/LUN/LUD/LUS Series: EL30, EL32, EL35, EL40, EL44, LH28RG, LH31G, LU28(A,R,G), LU32, LU35, LU38, LU46(A), LU50, LU54, LUN28, LUN30, LUD32, LUD35, LUS38 (Another significant engine brand commonly found in Japanese vessels).
NIIGATA:
- MG/M Series: MG40X(EX), M34X, 6M28BF, TM31X (Medium-speed diesel engines, typically used in small and medium-sized vessels).
MAK:
- M/MU/AK/AKM Series: M332, M453AK, MU551AK, MU552AK, M601, MU452AK, 451AK, 6M453AK, 9M453C, 6M601C, 8M601 (Medium-speed four-stroke engines, widely used in various marine applications).
WARTSILA:
- 20/22/26/32/38/46/GD/TKR Series: 22, 32, 31, 26, 20S, 28, 38, 46, 32GD, 46GD, 14, TKR22, HFR-V32, NOHAB (Wärtsilä’s broad portfolio of medium- and high-speed diesel engines for main propulsion, auxiliary, and generator sets).
DAIHATSU:
- PS/PKT/DS/DL/DK/PL Series: PS-18, PS-22, PS-20, PS-26, PS-30, PKT-14, PKT-16, PKTD-16, DS-18, DS-22, DS-26, DS-28, DS-32, DL-14, DL-16, DL-19, DL-20, DL-22, DL-24, DL-26, DK-20, PL-24 (Compact and reliable engines primarily used for auxiliary power and generator sets).
CUMMINS:
- BT/CT/NT/KTA/QSK/QSM Series: 4BT3.9, 6BT(A)5.9, 6CT8.3, NT(A)855, N14, KTA19, KTA38, KTA50, QSK19, QSM11 (Robust and durable engines for marine auxiliary power, generator sets, and some smaller main propulsion applications).
CATERPILLAR:
- 3000/3100/3300/3400/3500/3600 Series & C Series: 3054, 3056, 3066, 3106, 3126, 3306, 3406, 3408, 3412, 3508, 3512, 3516, 3606, 3608, 3612, 3616, 3618, C1.5, C2.2, C7, C9, C10, C12, C15, C16, C18, C30, C32 (Reliable and widely used engines across a vast range of main propulsion, auxiliary, and generator set applications).
SCANIA:
- DI Series: DI 09, DI 13, DI 16 (High-performance diesel engines designed for marine applications, typically used as auxiliary and smaller main propulsion engines).